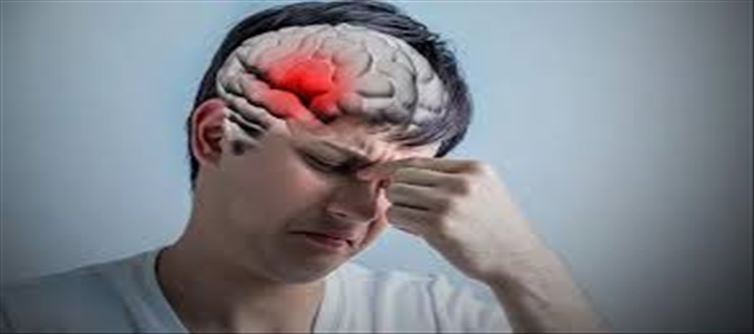
A stroke constitutes a medical emergency stemming from an interruption in the brain's blood supply, causing harm to brain cells. It is vital to be able to identify stroke symptoms swiftly to ensure immediate medical attention. There are two primary stroke types: ischemic and haemorrhagic, each featuring distinct signs.
.jpeg)
Ischemic strokes, the more prevalent variety, typically manifest as a sudden loss of strength or feeling, often affecting just one side of the body, encompassing the face, arm, or leg. Another characteristic indication is difficulty speaking or comprehending speech, resulting in slurred speech or challenges in forming coherent sentences. Visual disturbances, including abrupt blurred or loss of vision in one or both eyes, may also occur.
Conversely, haemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures. Indicators can encompass a sudden, severe headache that arises abruptly, frequently described as the most intense headache one has ever experienced. This may be accompanied by feelings of nausea, vomiting, and stiffness in the neck.
In both stroke categories, abrupt dizziness, loss of equilibrium, or problems with walking may emerge, along with a sudden and profound headache. Furthermore, individuals may experience confusion, coordination difficulties, and an overwhelming sensation of weakness or exhaustion. It is important to acknowledge that these symptoms can differ from one person to another, and not all may be present.




 click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel
click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel